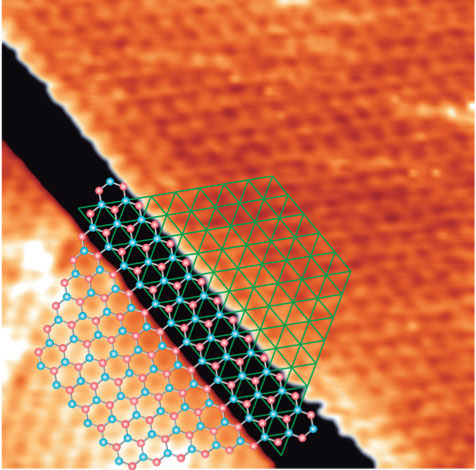
Figure I: Zoom-in of an edge region of a STM image of a triangular graphene island (TGI) with the image contrast set to show the atomic resolution on both graphene and Ni layers. The left part of the image corresponds to the graphene edge with a superposed honeycomb lattice (red and blue circles), the right part to the Ni(111) surface with a superposed hexagonal lattice (green mesh). The black stripe is a transition region related to the finite size of the tip where atomic resolution is missing.
Figure II: Relaxed model (top view) of the most stable configuration of TGIs on Ni(111) identified by DFT.
Figures taken from Garcia-Lekue, A., et. al. J. Phys. Chem. C, 111, 4072-4078 (2015).
DFT calculations reveal the most stable edge structures of graphene on Ni(111)
Motivation of the modeling
Edges play a fundamental role in shaping the morphology and electronic properties of graphene nanostructures. Electron confinement due to edge boundaries gives rise to energy band gaps, localized states, spin-polarization, and spin-dependent electron scattering. Furthermore, graphene edges determine the preferred sites for the attachment of metal atoms and chemical functionalization, as well as oxygen etching and intercalation.
Achievements of the model
A detailed insight into the interplay of substrate interaction and edge morphology is achieved thanks to the combination of experiments and theory. The most stable edge structures of graphene on Ni(111) as well as the role of stacking-driven activation and suppression of edge reconstruction are revealed.
Model system/Software
Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations, as implemented in the SIESTA and ANT.G codes, confirm and complement Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM) results. In summary, the following points were addressed:
The following key issues were investigated:
- Investigation of the structure, stability, and epitaxial relationship between the graphene edges
and a metallic substrate - Information on the edge stability and energetics
Juan Jose Palacios, part of the SIMUNE´s board of experts and developer of ANT.G is one of the authors of this work.